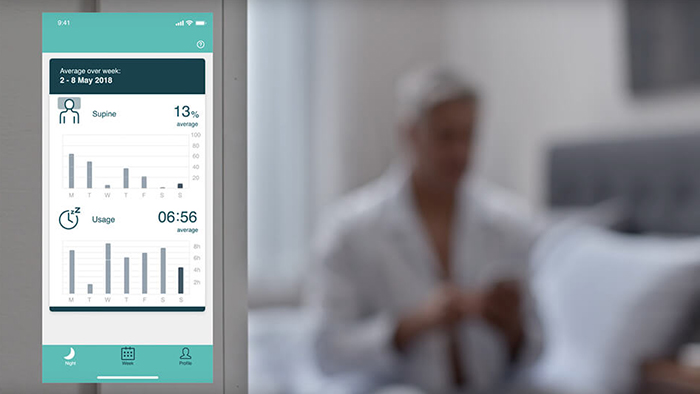
Find COVID-19 information specific to our Sleep and Respiratory Care solutions
NightBalance has been acquired by Philips.
Are you a healthcare professional?
Portals
Need more information?
For other information about the Philips NightBalance device please review this page or download the NightBalance brochure. For additional inquires please email support.nightbalance@philips.com

30-day money back guarantee
Financing available

30-day money back guarantee
Financing available
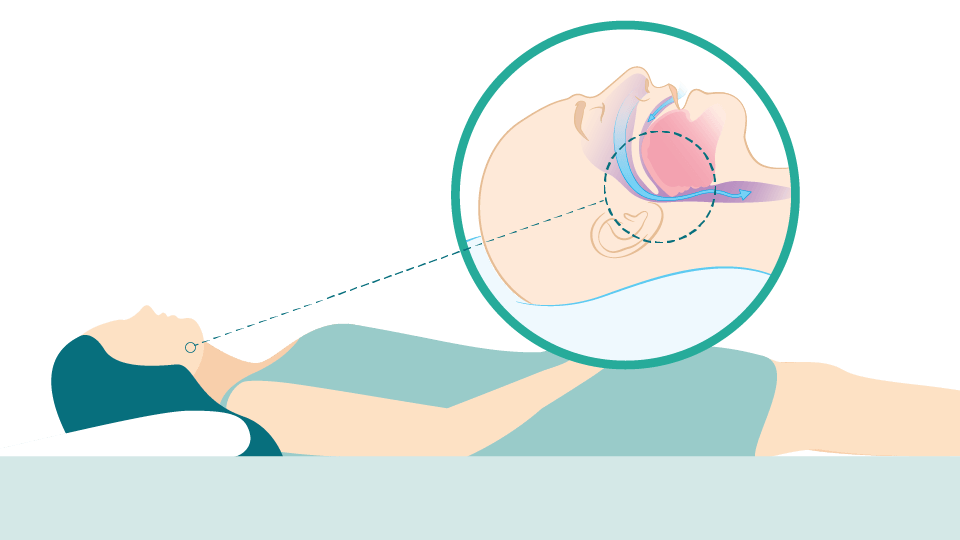
When you sleep on your back, your airway may be blocked, which can disrupt breathing.
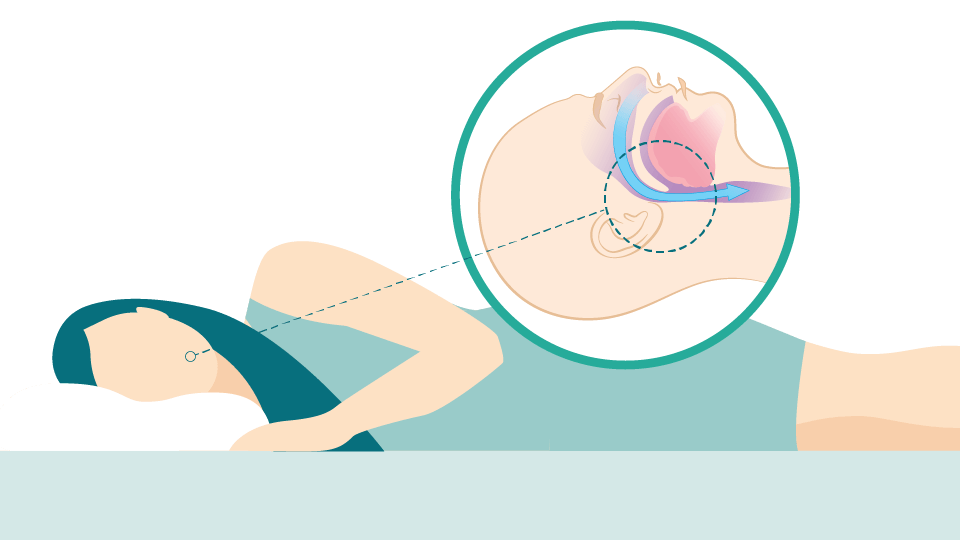
When you sleep on your side, your airway is clear, which allows for easy breathing.
We’re on your side with a mask-free sleep apnea therapy
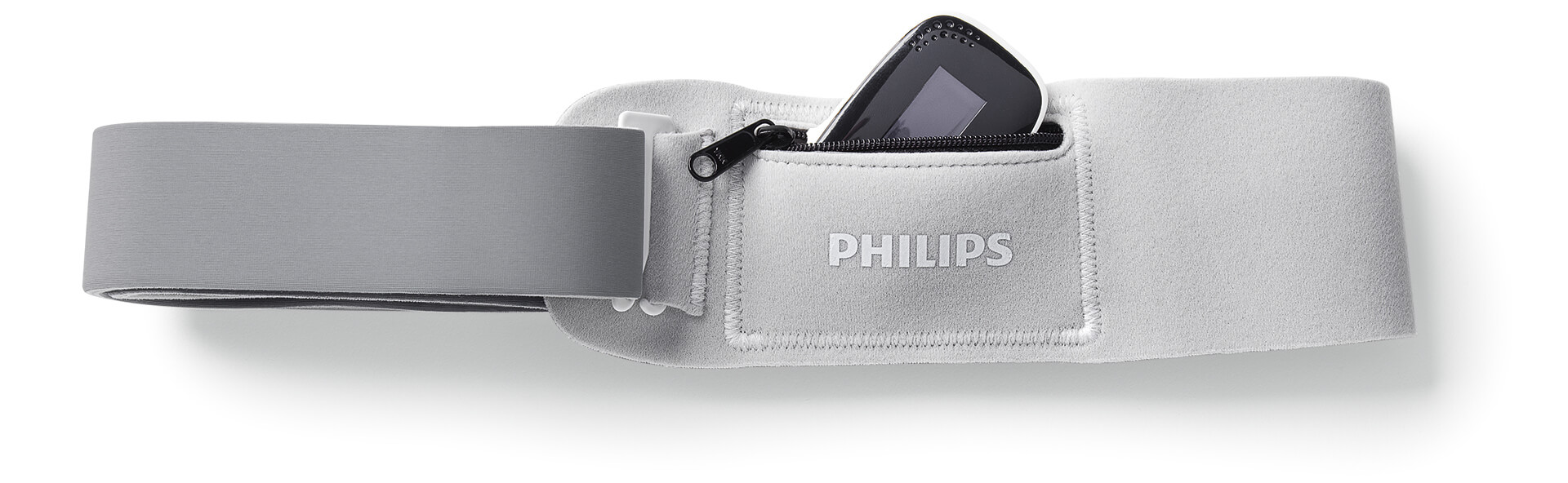
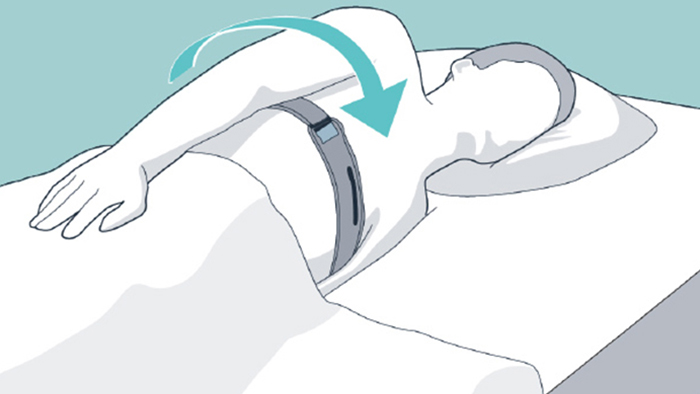
NightBalance is a compact, easy-to-use, mask-free treatment for positional OSA. The palm-sized device is worn comfortably across your chest in a soft, adjustable strap. NightBalance delivers gentle vibrations that prompt you to shift to your side without disturbing your sleep. It automatically adjusts the intensity of vibrations to provide the therapy you need.
NightBalance is:
Real results
More than 70% of people using NightBalance reported a long-term improvement in the three most reported positional OSA symptoms, including:2

Learn more about positional OSA and NightBalance

NightBalance:
-
NightBalance:
a closer look
NightBalance: a closer look
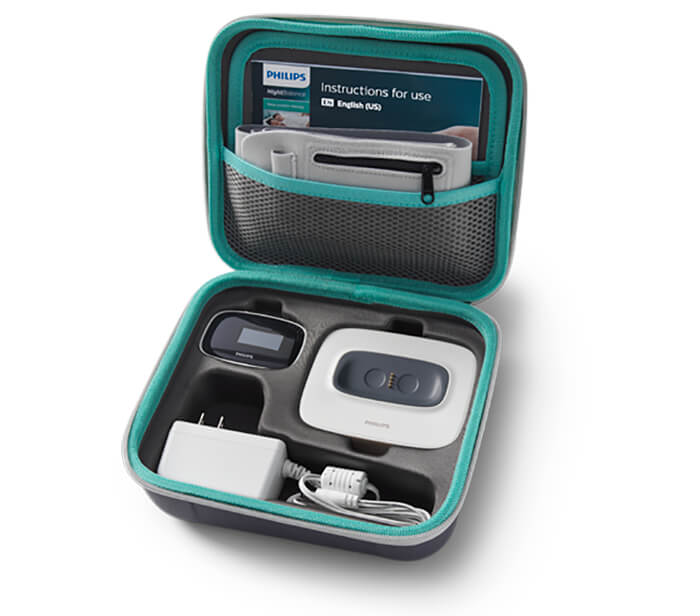
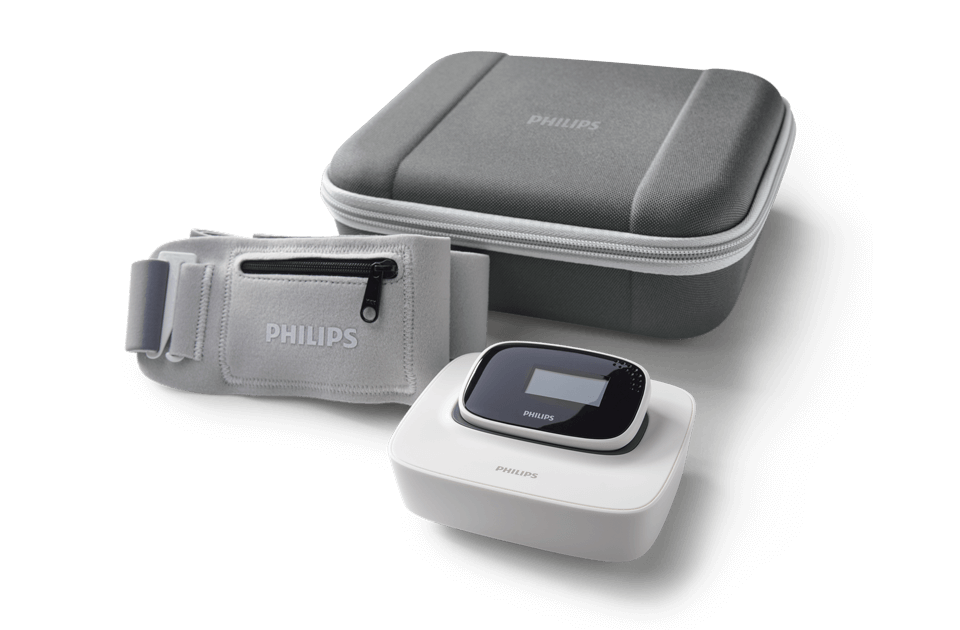
Travel case
Protective case for convenient traveling

Chest strap
Soft, adjustable chest strap has a pocket for the device
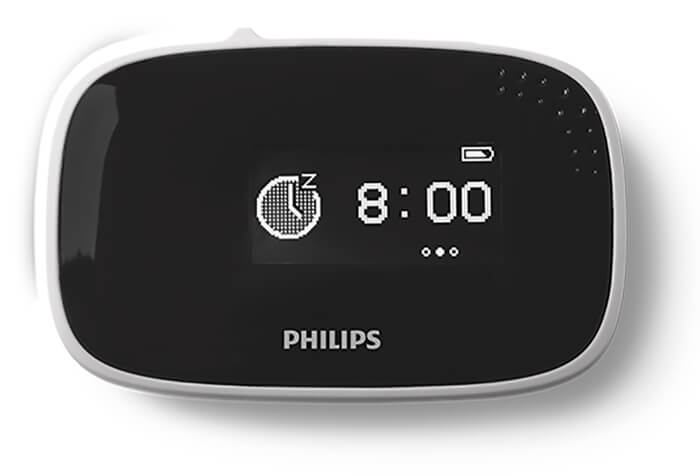

Sensor device
Small, lightweight sensor allows for easy data access
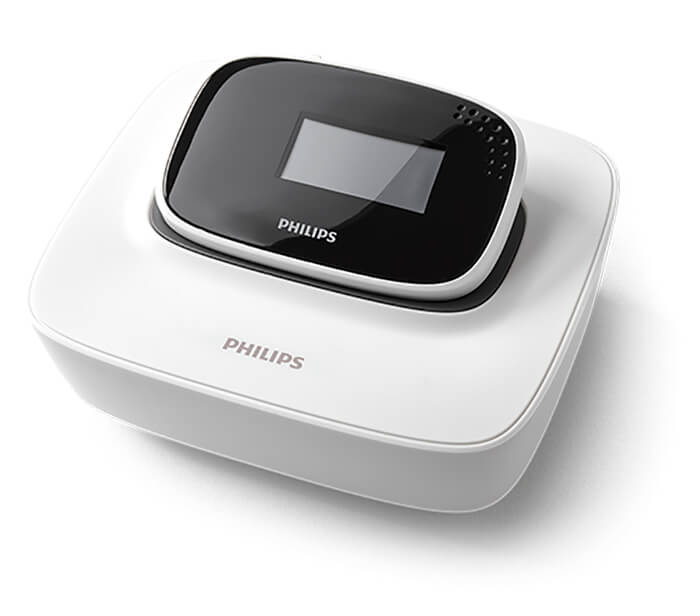

Docking station
Compact docking station for charging fits on a night table
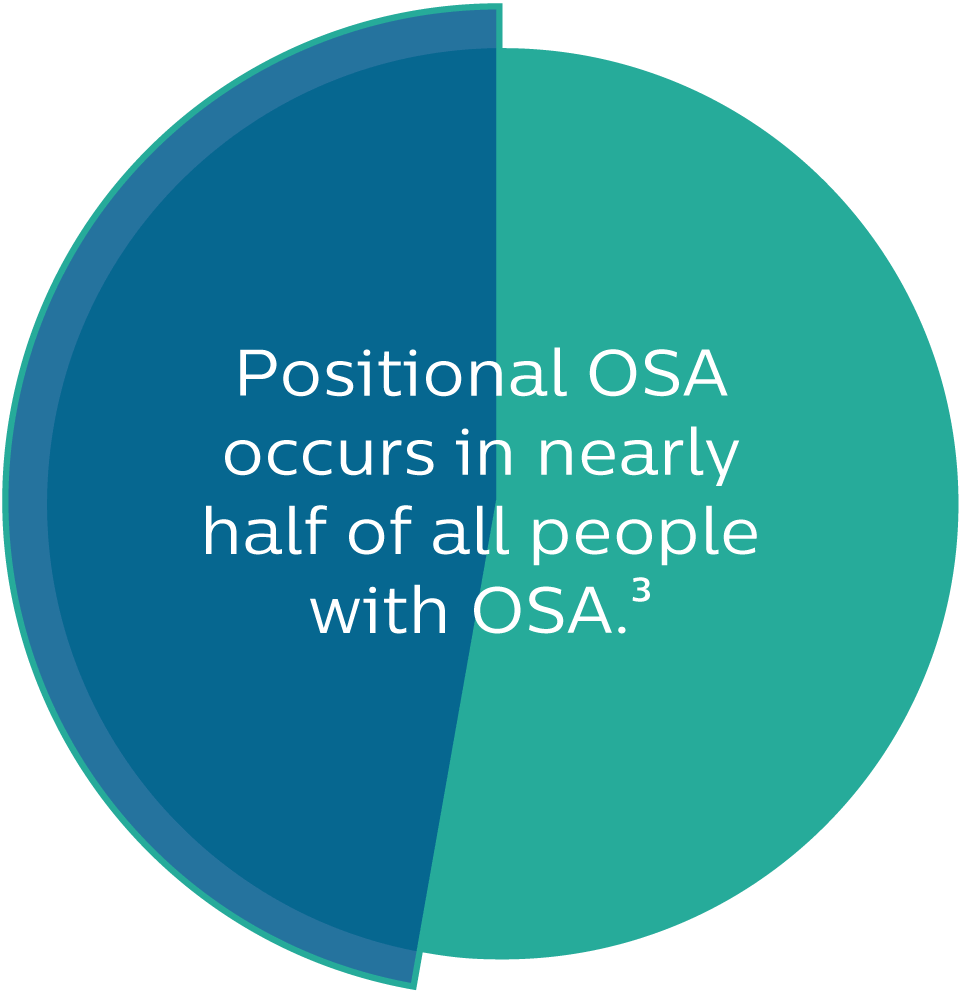
Positional OSA is more common than you might realize
Positional OSA is different than OSA. With positional OSA, most symptoms, like interrupted breathing, occur when you sleep on your back. If your sleep study reveals you have positional OSA, talk to your doctor about NightBalance.
Where to buy NightBalance
No results near you?
NightBalance resources
Getting started
Getting to sleep
Cleaning and care
Getting the most out of your device
Downloads
For additional questions, please contact customer service at 1-800-345-6443
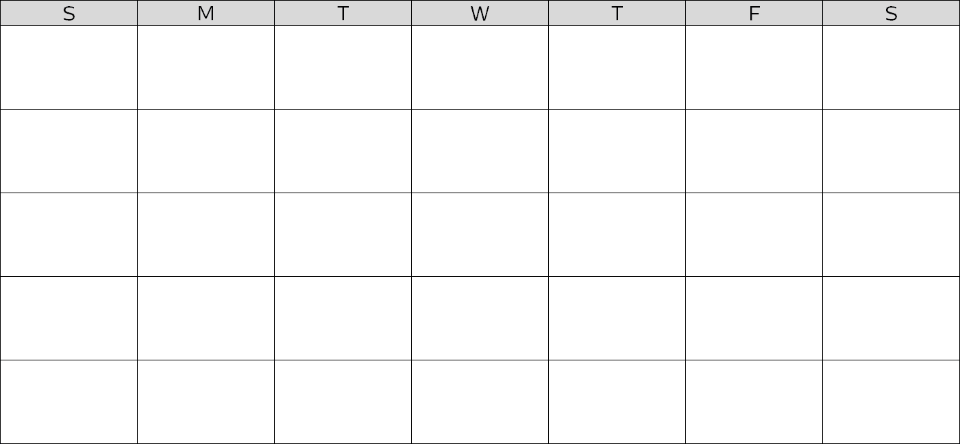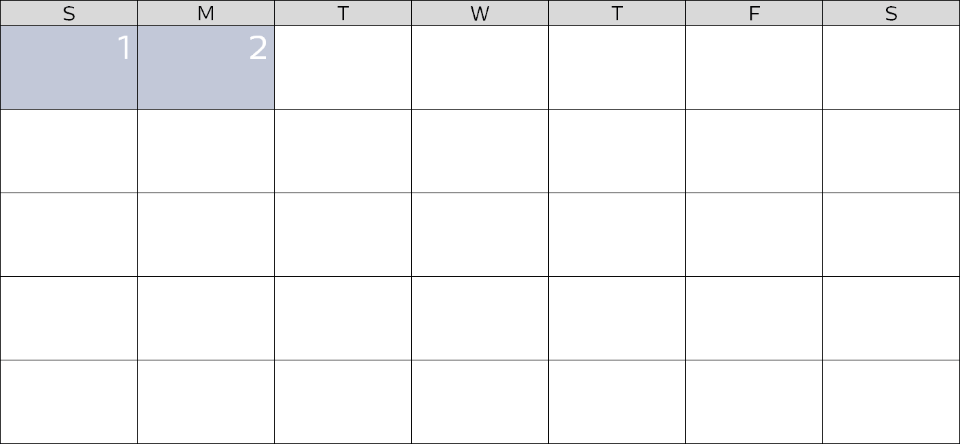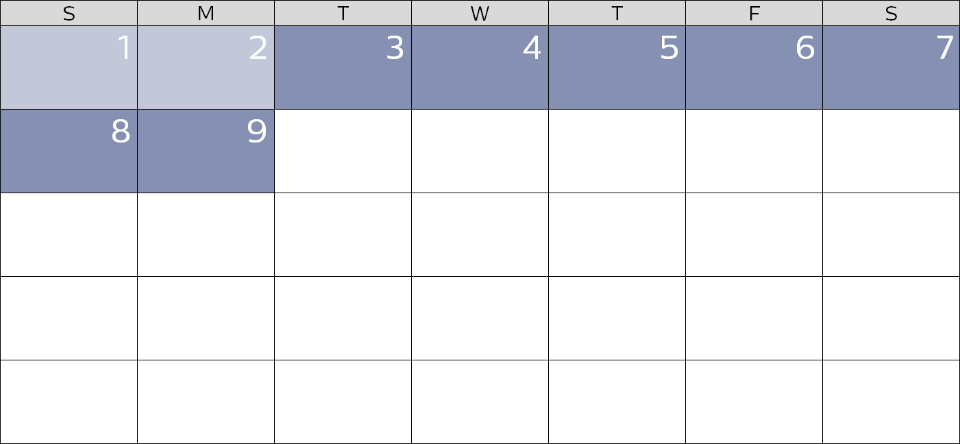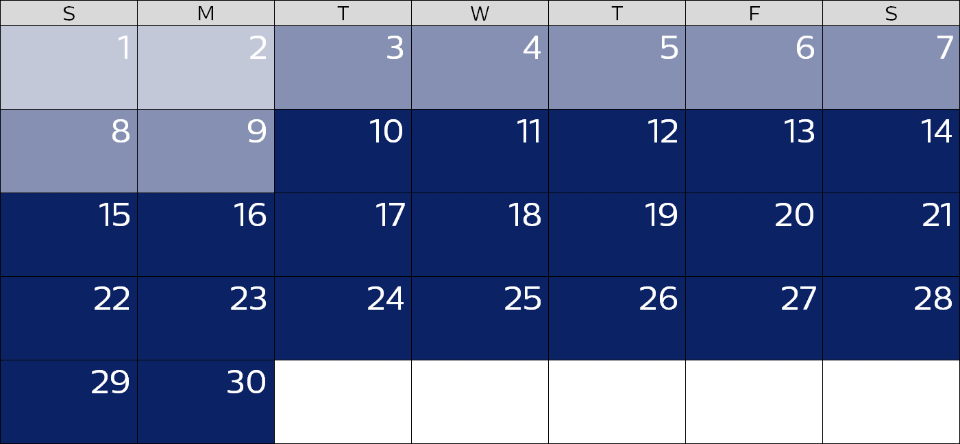
Adjust to your therapy
NightBalance uses an Adaptation Program to let you gradually adjust to POSA therapy.
For the first 2 nights, the device monitors your sleeping behavior with no therapy.
During nights 3-9, vibrations are gradually introduced over time to allow you to acclimate to the new POSA therapy.
On day 10 and forward, full treatment is delivered when therapy is needed – reducing the time spent sleeping on your back.5
Nightly use
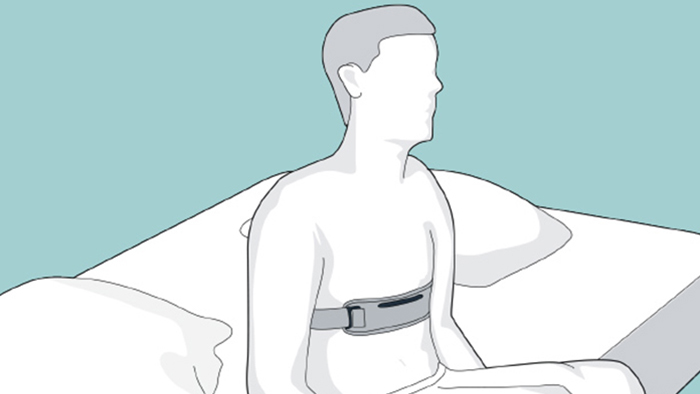
Patient can fall asleep in any position. After 15 minutes, the device activates and begins monitoring.
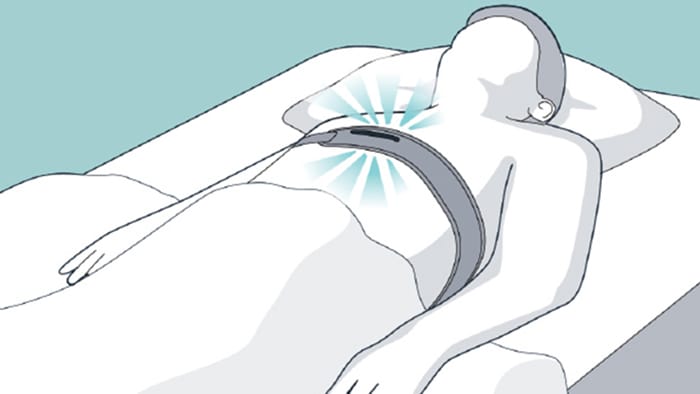
NightBalance detects when the patient is on their back. It prompts the patient to move off their back without disturbing their sleep.
Vibrations will stop when patient is on their side.
Medical advisory board
NightBalance is supported by an our medical advisory board, comprised of distinguished world renowned scientists and clinicians.

Prof. Dr. Nico de Vries

David P. White, MD

Dr. Raphael Heinzer

Jean-Louis Pepin, MD, PhD

Prof. Dr. Winfried Randerath, MD
Backed by clinical evidence
NightBalance is supported by years of clinical studies in patients with positional OSA.
Berry, R. et al, NightBalance Sleep Position Trainer Device Versus Auto-Adjusting Positive Airway Pressure for treatment of Positional Obstructive Sleep Apnea Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, Vol. 5, No.7, 947-956
Van Maanen et al, The sleep position trainer: a new treatment for positional obstructive sleep apnoea Sleep and Breathing (2013) 17:771–779
Van Maanen & de Vries, Long-Term Effectiveness and Compliance of Positional Therapy with the Sleep Position Trainer
SLEEP 2014; Vol. 37, No. 7
Eijsvogel etal, Sleep Position Trainer versus Tennis Ball Technique
Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine 2015; Vol. 11, No. 2
Dieljtens, A promising concept of combination therapy for positional obstructive sleep apnea
Sleep Breath 2015; 19:637–644
Benoist, Positional therapy in patients with residual positional obstructive sleep apnea after upper airway surgery
Sleep Breath 2016
Benoist, A randomized, controlled trial of positional therapy versus oral appliance therapy
Sleep Medicine 2017; 34:109e117
De Ruiter, Durability of treatment effects of the SPT versus oral appliance therapy in positional OSA: 12-month follow-up
Sleep Breath 2017
Laub, A Sleep Position Trainer for positional sleep apnea: a randomized, controlled trial
Journal of Sleep Research 2017
Frequently asked questions

Want to explore sleep apnea topics?

Are you a sleep professional?
Did you have a good experience with a Philips product? Help others like you.
1. Berry, R. et al, NightBalance sleep position treatment device versus auto-adjusting positive airway pressure for treatment of positional obstructive sleep apnea, J Clin Sleep Medicine,2019 ,Vol. 5, No.7, 947-956 2. NightBalance OSA Symptoms survey: Reimbursement Dossier Netherlands. 3. Heinzer, R. et al, Prevalence and Characteristics of Positional Sleep Apnea in the HypnoLaus Population-based cohort, Sleep Medicine 2018; 48:157-162. 4. Cartwright criteria, Effect of Sleep Position on Sleep Apnea Severity, R. Cartwright, 1984. 5. de Ruiter, M. et al, Durability of treatment effects of the sleep position trainer versus oral appliance therapy in positional OSA: a 12-month follow-up of a randomized controlled trial, Sleep and Breathing 201822:441-450.